Cost per acquisition, or CPA, is an online advertising pricing method where the advertiser pays for each specified acquisition (or action). For example, you can choose to pay $5 an impression, click, form submit, or sale. Depending on your budget, you can adjust the price you would like to pay per acquisition. Some businesses with a higher budget, for instance, can pay $25 per acquisition. CPA is the optimal way to buy online advertising because you only pay for the ad when the desired acquisition, determined by the advertiser, has occurred.
In a CPA pricing method, you must first know the objectives you want to achieve and therefore the acquisition you want to pay for and the amount you’re willing to pay for each acquisition. To learn where you can choose your objective and the amount you want to pay per acquisition when creating a Facebook ad, follow the steps below.
Step 1: Choose your objective
Go to business.facebook.com then go to Ads Manager. You can access Ads Manager by clicking the tab “Business Manager” on the upper left hand corner. Click “Ads Manager” on the drop-down menu.
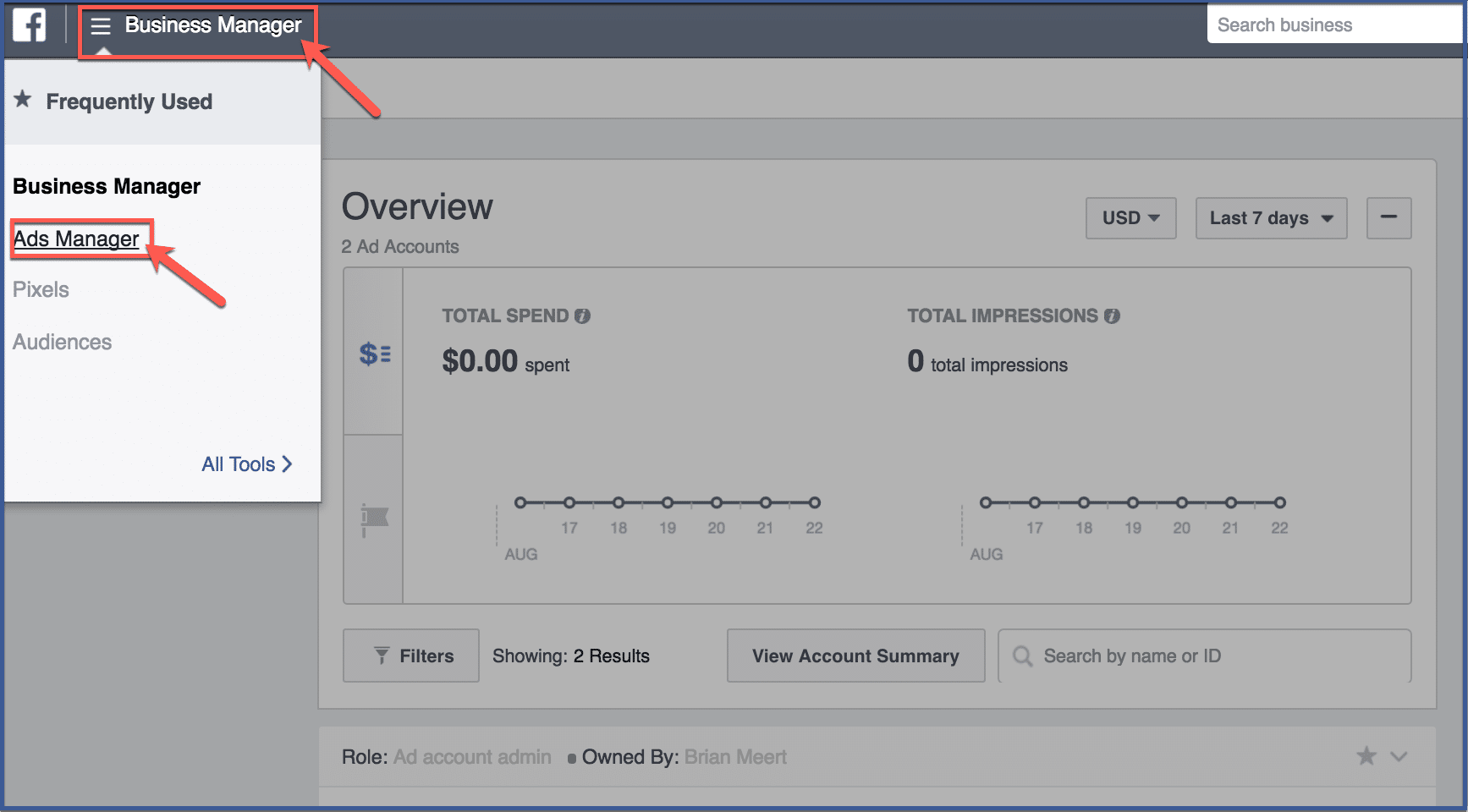
Step 2: Click “Create Ad”
Once Facebook takes you to Ads Manager, click “Create Ad“.
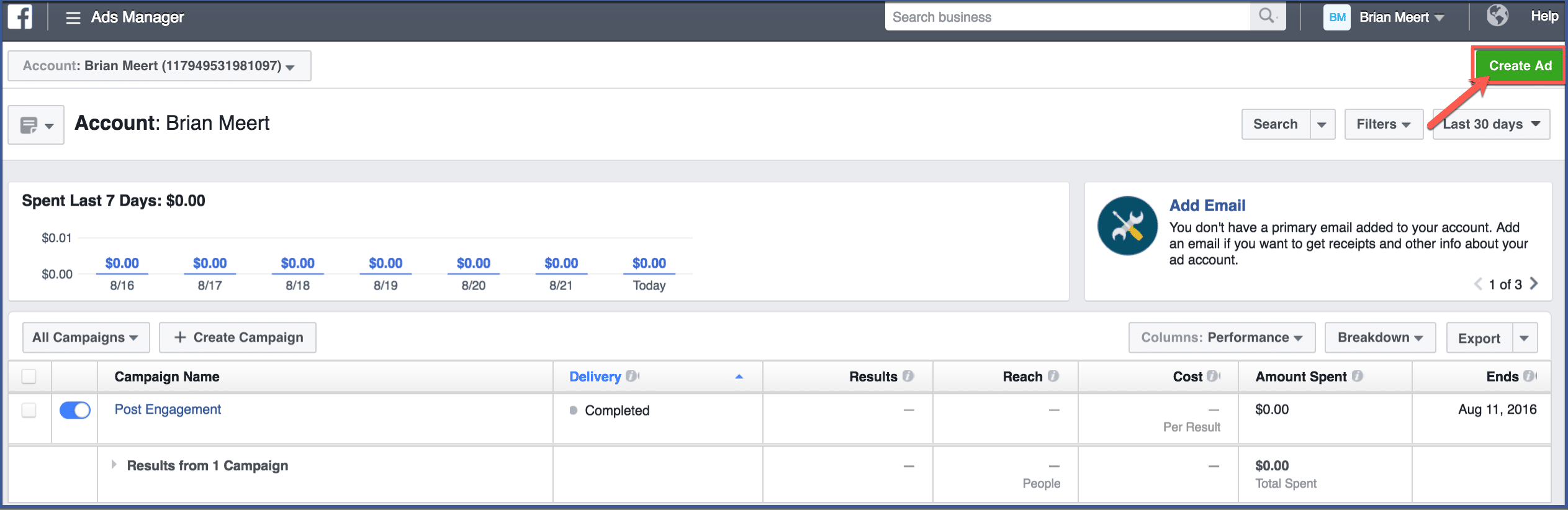
Step 3: Choose an objective
Before you can skip ahead to other fields, you must first choose an objective. An objective is your marketing goal. Ask yourself what you want your ad to do. Do you want it to direct users to your website, to promote your page, or to increase conversions? After choosing an objective, click “Continue“.
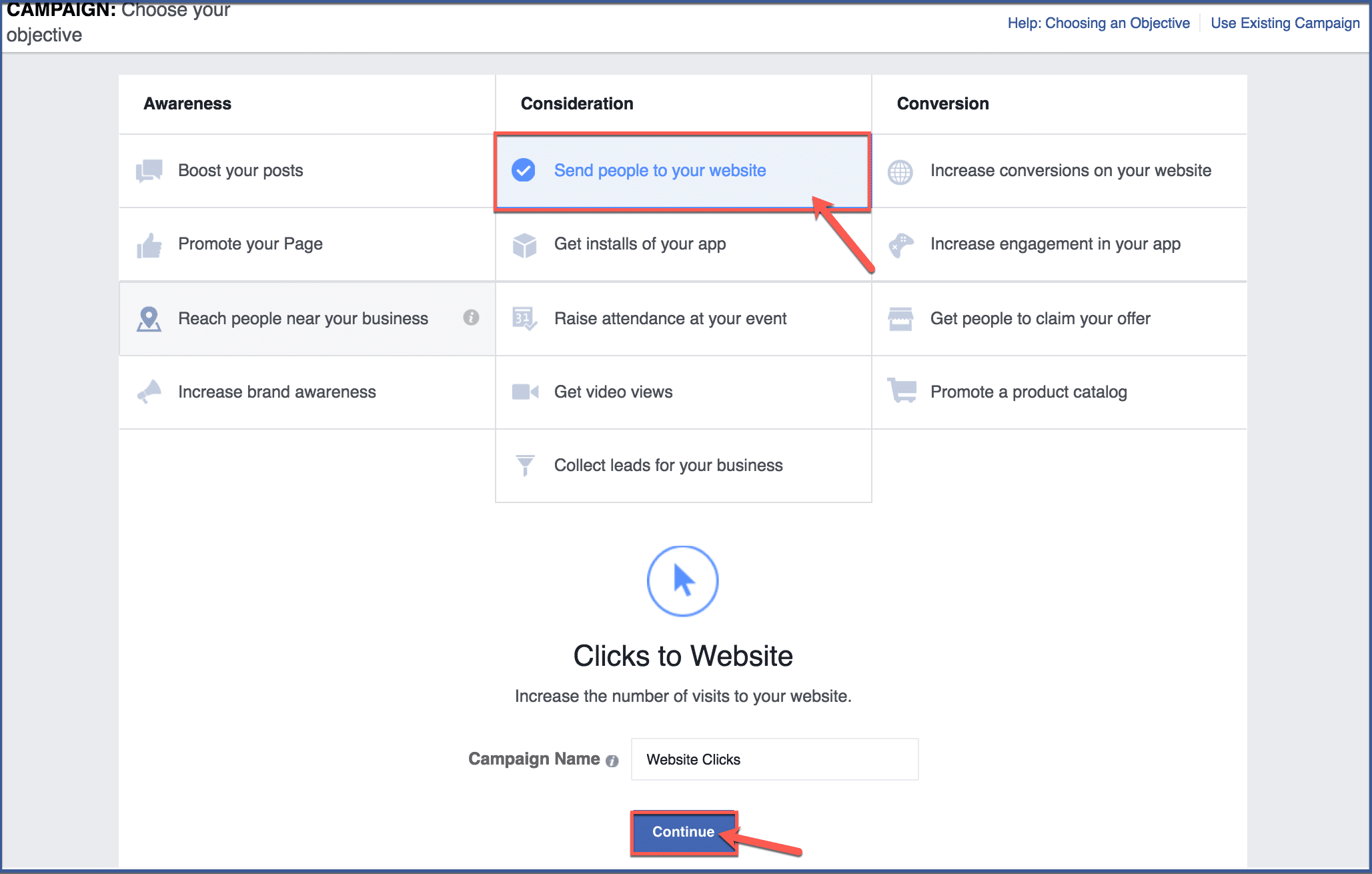
Step 4: Go to “Budget & Schedule”
Click “Budget and Schedule” on the left side of the screen under ad set. This is where you can choose how much you want to pay per acquisition and how you want Facebook to charge you. You can choose to pay per impression (the amount of times your ad is shown to people) or per click (the amount of times people click your ad. Clicks include clicking to comment, like, react, or go to your link).
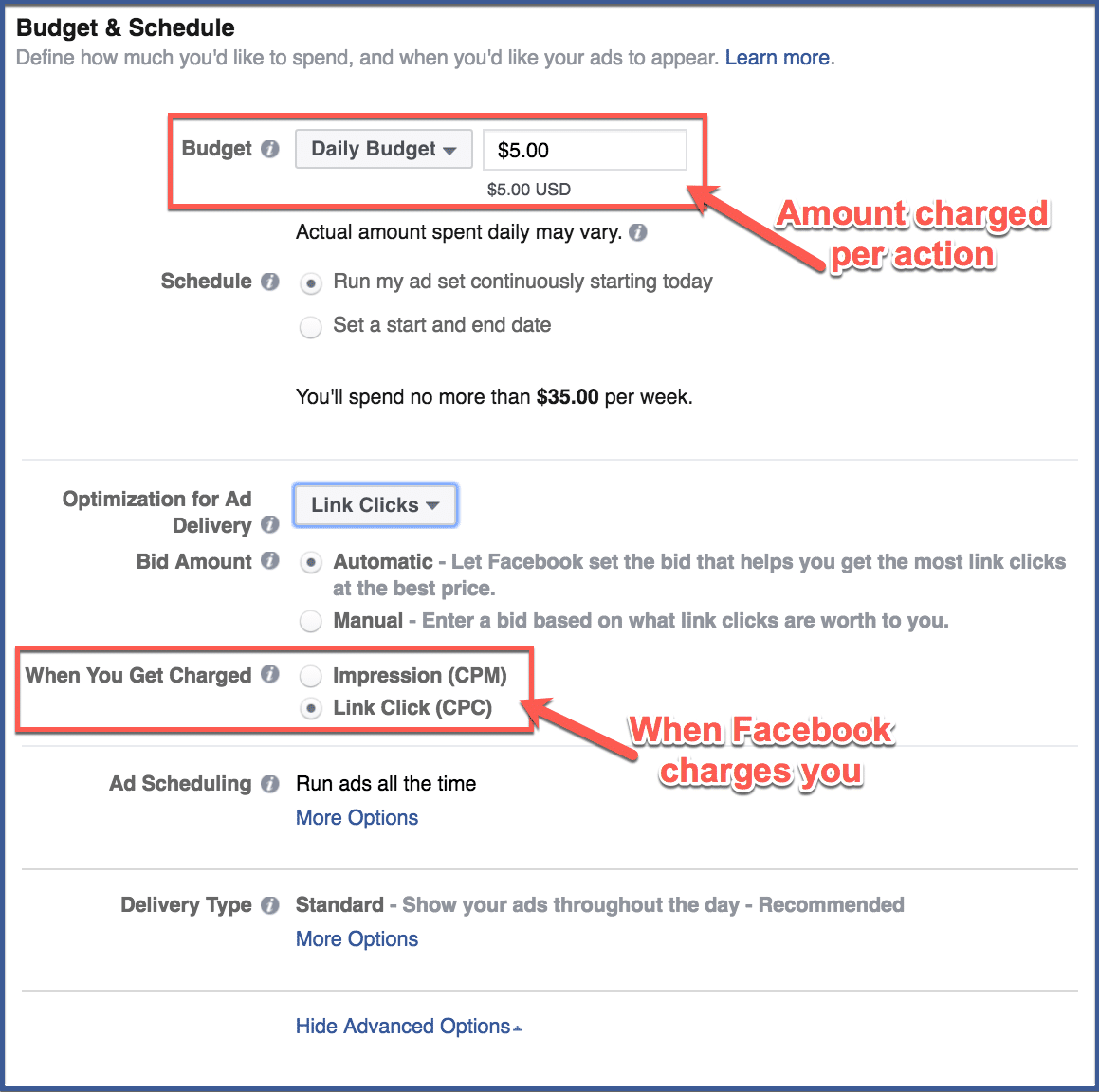
Why is CPA Important?
CPA provides advertisers with a concrete understanding of how effectively their campaigns are driving meaningful actions.
While high click-through rates may seem promising, they don’t necessarily translate to business success. Conversely, CPA zeroes in on the actual outcomes, helping advertisers gauge the campaign’s efficiency in converting potential customers into valuable actions.
Calculating Cost Per Acquisition
The formula for calculating CPA is straightforward: CPA = Total Cost of Campaign / Number of Conversions.
The total cost includes all expenses related to the campaign, such as ad spend, creative production, and any associated fees. The number of conversions refers to the desired actions that have been achieved as a result of the campaign.
Factors Affecting CPA
1. Ad Relevance and Quality
The quality and relevance of your ad play a significant role in determining the CPA. Highly relevant ads are more likely to resonate with the target audience, resulting in a lower CPA.
Advertisers should focus on crafting ad content that aligns with the audience’s interests and needs, driving higher engagement and conversions.
2. Target Audience
Reaching the right audience is paramount to achieving a low CPA. Precise audience targeting ensures that your ads are shown to individuals who are most likely to convert.
Defining your target audience based on demographics, interests, and behaviors can lead to more cost-effective acquisitions.
3. Ad Placement and Bidding Strategy
Where your ads appear, and the bidding strategy you choose can impact your CPA. Specific placements might yield better results than others, and bidding strategies can influence the cost of conversions. Experimenting with different placements and bidding strategies can help optimize CPA.
Types of Cost Per Acquisition?
There are different types of CPAs, depending on the desired outcome of the marketing campaign. Some of the most common types of CPA include:
- Cost Per Click (CPC): CPC, or cost-per-click, is a popular type of CPA (cost-per-action) in which advertisers pay for each click their ads receive. This metric is designed to increase website or landing page traffic. Advertised are only charged when users engage with the ad by clicking on it, regardless of whether they follow through with a conversion.
- Cost Per Lead (CPL): It measures the money spent on acquiring a potential lead or prospect. Advertisers are charged for each action taken by a user that shows interest, like filling out a contact form, subscribing to a newsletter, or signing up for a webinar. CPL is commonly utilized in B2B marketing and sales lead generation.
- Cost Per Sale (CPS): CPS, also known as Cost Per Order (CPO), calculates the cost of each confirmed sale resulting from an advertising campaign. Advertisers pay a predetermined commission for every completed purchase. CPS is commonly used in e-commerce and affiliate marketing programs.
- Cost Per Install (CPI): CPI applies to mobile app advertising, where advertisers pay for each instance a user successfully installs an app. This metric is crucial for app developers looking to acquire a user base. CPI campaigns are common in the app industry, often promoting games, utilities, and other mobile applications.
- Cost Per View (CPV): CPV is relevant for video content advertising, where advertisers pay for each view of their video ad. Unlike CPC, which requires a click, CPV is charged based on video views, making it suitable for brand awareness and engagement campaigns.
- Cost Per Engagement (CPE): CPE tracks the cost of user engagement with a specific element within an ad, such as clicking a call-to-action button, interacting with a poll, or expanding a video. Advertisers pay when users interact with these engaging elements.
Strategies to Optimize CPA
1. Refine Audience Targeting
Identifying your ideal customer segments is crucial. Use Facebook’s robust targeting options to focus your ads on individuals who are more likely to convert. This precision helps reduce ad spend wastage and enhances the likelihood of achieving a lower CPA.
2. Ad Creative and Messaging
Invest time and effort in creating compelling ad creatives and clear messaging. Engaging visuals and persuasive calls to action can encourage users to take the desired actions. A well-crafted ad can lead to higher click-through rates and conversions, ultimately improving your CPA.
3. Landing Page Optimization
Your landing page plays a pivotal role in converting clicks into valuable actions. Ensure that your landing page is user-friendly, relevant to the ad content, and optimized for mobile devices. A seamless user experience can boost conversions and contribute to a lower CPA.
Measuring Success and Adjusting Strategies
1. Benchmarking CPA
To gauge the success of your campaigns, it’s essential to establish a benchmark CPA based on industry standards and campaign goals. This benchmark serves as a reference point for evaluating your campaign’s performance and identifying areas for improvement.
2. Monitoring and Iterating
To ensure success in your campaigns, consistently monitoring and adjusting is essential. Keep track of your CPA and analyze the data regularly. Look for patterns, evaluate the effects of changes, and use data-driven insights to fine-tune your strategies for optimal results.
Final Thoughts
CPA is an important metric that advertisers can use to track the effectiveness of their Facebook marketing campaigns.
By understanding how much they are spending to acquire new customers, advertisers can make decisions about how to allocate marketing budgets and to improve the efficiency of their campaigns.
FAQs
What is Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)?
Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) refers to the average cost incurred to acquire a specific action, such as a purchase, sign-up, or download, through your ad campaigns. It gives a clear picture of how efficiently your campaigns are driving valuable actions rather than just clicks or impressions.
How is CPA calculated?
To calculate CPA, you divide the total cost of your ad campaign by the number of conversions achieved. The formula is: CPA = Total Cost / Number of Conversions. Conversions represent the desired actions, such as purchases or sign-ups, that users take as a result of interacting with your ads.
Why is understanding CPA important for advertisers?
Understanding CPA is crucial because it reveals your ad campaigns’ actual impact in driving meaningful actions. Instead of focusing solely on clicks or views, CPA helps you measure your campaigns’ efficiency in generating real results, such as sales or leads.
What factors can influence the CPA?
Several factors can influence CPA in Facebook advertising. These include the relevance and quality of your ads, the targeting of your audience, the ad placements you choose, the bidding strategy you employ, and the effectiveness of your ad creatives and landing pages.
How can advertisers optimize their campaigns based on CPA on Facebook?
Advertisers can optimize their campaigns based on CPA by refining their audience targeting, creating compelling ad creatives, and ensuring their landing pages are user-friendly and relevant. Regularly monitoring CPA metrics and adjusting campaigns based on performance trends is key to achieving a lower CPA and better results.
Recommended Articles Related to Facebook Advertising:
